2.1 The Level of Economic Activity

THE LEVEL OF OVERALL ECONOMIC ACTIVITY – TOPICS:
- Economic activity
- Measures of economic activity
- The business cycle
Economic Activity

By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income between households and firms in a closed economy with no government.
- Identify the four factors of production and their respective payments (rent, wages, interest and profit) and explain that these constitute the income flow in the model.
- Outline that the income flow is numerically equivalent to the expenditure flow and the value of output flow.
- Describe, using a diagram, the circular flow of income in an open economy with government and financial markets, referring to leakages/withdrawals (savings, taxes and import expenditure) and injections (investment, government expenditure and export revenue).
- Explain how the size of the circular flow will change depending on the relative size of injections and leakages.
|
What is the circular flow?
Basically the circular flow of income and spending shows connections between different sectors of an economy
|
|
|
|
|
How is Economic Activity Measured?
Measures of Economic Activity examines the various measures of national income. Gross domestic product (GDP) is the dominant statistic that countries use to measure economic activity. Gross national income (GNI) and gross national product (GNP) are also outlined. We make a distinction in IB Economics between real and nominal GDP, and GDP per capita. We will evaluate the usefulness of these national income statistics.

THE LEVEL OF OVERALL ECONOMIC ACTIVITY – TOPICS:
- What is GDP?
- How do we measure GDP?
- Distinguish between GDP, GNP and GNI
- What is net national product?
- Distinguish between nominal GDP and real GDP
- Outline GDP per capita
- Evaluate the usefulness of national income statistic
Measures of Economic Activity
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Distinguish between GDP and GNP/GNI as measures of economic activity.
- Distinguish between the nominal value of GDP and GNP/GNI and the real value of GDP and GNP/GNI.
- Distinguish between total GDP and GNP/GNI and per capita GDP and GNP/GNI.
- Examine the output approach, the income approach and the expenditure approach when measuring national income.
- Evaluate the use of national income statistics, including their use for making comparisons over time, their
use for making comparisons between countries and their use for making conclusions about standards of living. - Explain the meaning and significance of “green GDP”, a measure of GDP that accounts for environmental destruction.
GDP vs GNP
|
|
The Business Cycle
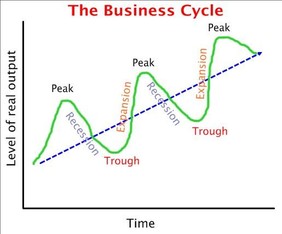
The Business Cycle section within the Level of Overall Economics IB Economics topic, examines the recurring fluctuations in an economy's economic activity. There is a regular, repeating pattern (or cyclical pattern) in overall economic activity and this is examined in IB Economics. The business cycle examines the long-term trend in real GDP. GDP increases over time but does not do so smoothly. There are economic expansions, downturns, recessions and peaks to economic activity.
BUSINESS CYCLE – TOPICS:
BUSINESS CYCLE – TOPICS:
- Understanding the business cycle
- Explaining the relationship between an economy's real GDP and time
- Identifying the cyclical pattern an phases of the business cycle
- Understanding the long-term growth trend
- Identifying potential economic output
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the business cycle.
- Explain the long-term growth trend in the business cycle diagram as the potential output of the economy.
- Distinguish between a decrease in GDP and a decrease in GDP growth.
The Business Cycle Explained

Recession – A period of decreasing economic activity (also known as an economic contraction or downturn) during which:
Trough – A period of economic activity during which:
Recovery – A period of increasing economic activity during which:
Peak – A period of very active economic activity where real GDP growth is growing at its fastest rate, during which:
- Unemployment is increasing
- Investment is decreasing and more business failures
Trough – A period of economic activity during which:
- Significant numbers of unemployed
- Very low levels of business confidence
- A slowing of price rises
Recovery – A period of increasing economic activity during which:
- Unemployment is falling
- Investment is taking place
- Prices are rising
Peak – A period of very active economic activity where real GDP growth is growing at its fastest rate, during which:
- Unemployment is at its lowest
- Investment is at its highest
- An economy experiences the largest rate of increase in the prices of goods and services.
Crash Course: 2008 Financial Crisis |
2008 Causes and Effects |
|
|
|
