Unit 2: 600C.E to 1450
During this unit change occurred for many reasons, but three phenomena were mainly responsible for it were:
Mass migrations
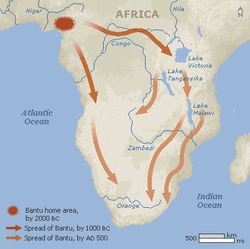
Whenever a significant number of people leave one area and migrate to another, change occurs for both the land that they left as well as their destination. (E.G. Bantu-speaking people originally lived in an area south of the Sahara, but probably because the desert was spreading southward they began to migrate to better land. They spread south and east into many parts of Africa, and their language became a basis for the formation of many later languages. The Bantu Migration is generally believed to be a major source for Africanity, or a set of cultural characteristics (including language) that are commonly shared on the continent. Examples include music, the use of masks, and scarification (permanent beauty etchings on the skin).
Mass migrations
Whenever a significant number of people leave one area and migrate to another, change occurs for both the land that they left as well as their destination. (E.G. Bantu-speaking people originally lived in an area south of the Sahara, but probably because the desert was spreading southward they began to migrate to better land. They spread south and east into many parts of Africa, and their language became a basis for the formation of many later languages. The Bantu Migration is generally believed to be a major source for Africanity, or a set of cultural characteristics (including language) that are commonly shared on the continent. Examples include music, the use of masks, and scarification (permanent beauty etchings on the skin).
Imperial conquests
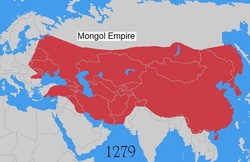
If an empire (or later a country) deliberately conquers territory outside its borders, significant changes tend to follow for both the attackers and the attacked. (E.G. The Mongol conquests have been depicted as assaults by savage and barbarian people who brought nothing but death and destruction to the areas they attacked. Whereas no one can deny the brutality of the Mongols, their conquests had a much more varied impact on world history than has been acknowledged by many historians in the past. At the peak of their power, the Pax Mongolica meant that once-hostile people lived together in peace in areas where most religions were tolerated. From the Il-Khan in the Middle East to the Yuan Dynasty in China, Mongol rulers established order, and most importantly, provided the stage for intensified international contact. Protected by Mongol might, the trade routes carried new foods, inventions, and ideas from one civilization to ther others, with nomadic people acting as intermediaries.
Cross-cultural trade and exchange
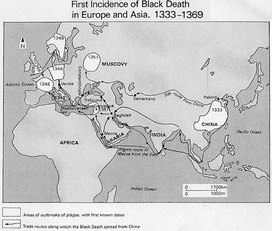
Widespread contact among various areas of the world brings not only new goods but new ideas and customs to all areas involved. Cross-cultural exchanges had deadly consequences for many parts of the eastern hemisphere during the 14th century. As Eurasians traveled over long distances, they not only exchanged goods and ideas, but they unwittingly helped disease to spread as well. Since people who have had no previous exposure to a disease react to it much more seriously than those that have, the consequences were profound. The bubonic plague erupted in epidemics throughout most of Asia, Europe, and north Africa. Even though it abated in subsequent centuries, it broke out sporadically from place to place well into the seventeenth century.
The plague probably originated in southwestern China, where it had been incubating for centuries, but once long-distance trade began, it spread rapidly during the 14th century. The virus was spread by fleas that infested rats and eventually humans. Mongol military campaigns helped the plague spread throughout China, and merchants and travelers spread it to the west. By the 1340s it had spread to Black Sea ports and to Italian cities on the Mediterranean. From there, the plague spread rapidly throughout Europe as far as the British Isles.
Europeans referred to the plague as the Black Death because its victims developed black or purpose swellings caused by buboes, internal hemorrhages that gave the plague its name. Once the plague hit a community, typically 60-70 percent of the population died, and in some cases, no one survived.
The plague probably originated in southwestern China, where it had been incubating for centuries, but once long-distance trade began, it spread rapidly during the 14th century. The virus was spread by fleas that infested rats and eventually humans. Mongol military campaigns helped the plague spread throughout China, and merchants and travelers spread it to the west. By the 1340s it had spread to Black Sea ports and to Italian cities on the Mediterranean. From there, the plague spread rapidly throughout Europe as far as the British Isles.
Europeans referred to the plague as the Black Death because its victims developed black or purpose swellings caused by buboes, internal hemorrhages that gave the plague its name. Once the plague hit a community, typically 60-70 percent of the population died, and in some cases, no one survived.
Sample Classroom Activities
Below is a PowerPoint I use whilst giving an introductory lecture on Classical Amerindian Civilizations. In order to make this a more interactive learning experience students collaboratively take notes via Google Documents.
Cultural Interactions during Unit II (600-1450)
Download the following cultural interactions chart from Unit II and complete it as best you can. It has been partly completed for you to give an idea / an example of how to complete it. Do not worry if you find yourself repeating information. It is almost impossible not to!
Unit 2 Review Materials
|
Analyze continuities and changes in patterns of interaction along the Silk Road 200BCE to 1450CE
|
A very detailed PowerPoint review created by the excellent Bill Strickland
| ||||
|
Completing CCOT charts will help you prepare for the CCOT Free Response Question on the Exam. Choose a world region, e.g. Europe and complete the chart as best you can. You'll be surprised at how much you know!!!
|
Review Packet for Unit II
| ||||
