01 Human beginnings and early civilizations
What will we study?

By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Define the term prehistory.
- Understand how artifacts can be used to gain an understanding of the way of life of early humans
- Understand the influence of physical geography on the lives of early humans and their development
- Interpret a map to describe early human migration across the globe
- Distinguish between characteristics of the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods
- Recognize and analyze changes and continuities over time from the Paleolithic to the Neolithic
- Identify and explain characteristics of a civilization
- Understand the drawbacks of civilization compared to non-civilized societies
- Evaluate why the term “civilization” is a connotative word
Unit oveview

During this unit we will begin at looking at Early Humans and the importance of geography and climate in influencing their innovations and migratory patterns. We will at when, how, and why did people give up their wandering and settle to live in one place? Initially, it happened in different parts of the world at different times, but settled communities had developed in many places by 8000 BCE. The ability to settle was based almost entirely on successful cultivation of crops and the domestication of animals. These drastic changes in human life are known collectively as the Neolithic Revolution that almost certainly happened independently in different places over a large span of time.
The Neolithic Revolution is arguably the most important event in human history. It led to an increase in reliable food supplies which led to a rapid increase in total human population. As a result occupations other than farming developed, since fewer people were needed to produce food. Gender differences increased, as men took over most agricultural cultivation and domestication of animals. Women were responsible for raising children, cooking food, and keeping the house, but in virtually all of the early civilizations men became more and more dominant. A patriarchal system commonly developed, with men holding power in the family, the economy, and the government. Finally a clear distinction was created with those who did not grow crops and remained nomadic and those who settled in one area and later built the first civilizations.
The Neolithic Revolution is arguably the most important event in human history. It led to an increase in reliable food supplies which led to a rapid increase in total human population. As a result occupations other than farming developed, since fewer people were needed to produce food. Gender differences increased, as men took over most agricultural cultivation and domestication of animals. Women were responsible for raising children, cooking food, and keeping the house, but in virtually all of the early civilizations men became more and more dominant. A patriarchal system commonly developed, with men holding power in the family, the economy, and the government. Finally a clear distinction was created with those who did not grow crops and remained nomadic and those who settled in one area and later built the first civilizations.
Where did early humans come from?
So what was life like in for early humans?
|
|
|
Why did neanderthals die out and homo sapiens thrive?
Pre-historic cave paintings in France
In the Ardeche gorge in southern France lies one of the most important prehistoric sites ever discovered. It's locked away behind a thick metal door, hidden halfway up a towering limestone cliff-face. Few people have ever been allowed inside, but BBC Newsnight has been granted rare access by the French Ministry of Culture and Communication. This artwork is more than 30,000 years old!
The emergence of civilizations
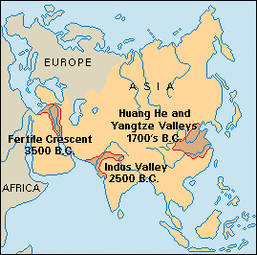
These changes brought about by the Neolithic Revolution turn allowed the development of civilizations. However the how to define a civilization can be complex and emotive. Former American President George Bush would often talk about the 'civilized' and 'uncivilized' during speeches he made whilst being President. How would you feel if you were described as being 'uncivilized'? What does the word 'civilized' mean to you? To some it means being more 'advanced' than others that remain more 'backward'.
During our study of some the world's first civilizations we will examine their common characteristics and differences. But most importantly we will investigate why they might have been similar and why they were different.
Being able to identify similarities and differences between different societies and then being able to explain those similarities and differences occur is a MAJOR part of studying History in high school.
During our study of some the world's first civilizations we will examine their common characteristics and differences. But most importantly we will investigate why they might have been similar and why they were different.
Being able to identify similarities and differences between different societies and then being able to explain those similarities and differences occur is a MAJOR part of studying History in high school.
Characteristics of Early Agricultural Civilizations
It is imperative that you know and understand the common characteristics of early agricultural civilizations. Note that the characteristics mentioned below expand on the definition of a civilization.
|
Characteristic
Permanent settlements Specialized workers Technological innovations Governments Social Classes Religion |
Significance
As people began to farm, they began to settle in one place. Eventually, villages, towns, and cities developed. Important examples of early permanent settlements are Catal Huyuk and Jericho. Early cities became the focus of a civilization because of their political, cultural, and economic importance As farming produced food surpluses, many people did not have to farm and were able to specialize in other areas, such as ceramics and textile production. As civilizations advanced, people were able to specialize in other professions, such as commerce, civil engineers, religious leaders, and political leaders Early agricultural/Neolithic civilizations developed the use of various metals (copper, gold, and bronze in that order) for items such as weapons and other luxury goods; other examples of technological innovations, largely due to the specialization of workers, include advanced irrigation apparatus, the wheel, weapons, sundials, etc. As cities developed in the early civilizations, the inhabitants required large public works projects beyond the scope of private citizens. As a result, governments formed to organize and oversee the fabrication of roads, irrigation projects, public buildings, etc. and to regulate commerce (through the establishment of laws, courts, and a system of punishment. Moreover, governments functioned to protect citizens from invasions and to organize attacks on rival civilizations. Governments also collected taxes from the city dwellers As people settled on land to farm, there were those who laid claim to more land than others, thus forming the first elite social classes. Early civilizations had an elite social class comprised of large land-owners. Many civilizations, such as Sumer, had a slave class, although in most cases slaves could buy their freedom. Likewise, men could sell women and children into slavery to pay off debts. As people began to observe more closely their environment in an effort to increase agricultural productivity, knowledge of seasons and nature increased. Attempting to explain natural processes and natural disasters, people developed elaborate stories about the origin of life and rituals to appease gods they perceived as controlling nature. Over time, a group of specialized workers emerged to lead these rituals and devote their lives to the worship of deities. |
Why is Islamic State trying to destroy the ancient city of Palmarya?
|
|
|
|
|
|
Why should we care?
Ancient Palmyrene art, monuments, temples, cemeteries and statues are among Syria's - and the world's - most treasured artefacts. Syrian Interior Minister Mohamad Al-Shaar said hundreds of statues have already been removed from Palmyra to pre-empt the IS takeover. "We will make all possible efforts to maintain this large stock (of antiquities) and we will give this the greatest importance because, as we said, this is the inheritance for the nation and for humanity," he said. The ruins at Palmyra had already been placed on the UNESCO World Heritage "in danger" list in 2013.
Dr Steven Bourke, an archaeology researcher at the University of Sydney who's led multiple ongoing excavations at historic sites in the Middle East, says the new risk to what is one of the ancient world's most culturally significant sites cannot be understated. "Well, it's catastrophic," Dr Bourke said. "It's our history, it's the history of all humankind that's at risk here. It's the history of the peoples of the Middle East, it's the history of the Arab peoples, it would be the pre-history of the state that's trying to form itself in that area. It's to understand where people came from, how they developed into who they were, what are the major key advances, when did they occur and how we got to be who we are. So, Palmyra has material bearing on all of those questions. The antiquities of the past are important, but so are the people living there today and our major concern should be for the living," Dr Bourke says. "Though the living are the ones who are going to need evidence of the past when they start rebuilding their country."
Dr Bourke said archaeologists both within Syria and internationally have been risking their lives to protect Syrian antiquities by keeping an eye on international markets for any stolen items.
Dr Steven Bourke, an archaeology researcher at the University of Sydney who's led multiple ongoing excavations at historic sites in the Middle East, says the new risk to what is one of the ancient world's most culturally significant sites cannot be understated. "Well, it's catastrophic," Dr Bourke said. "It's our history, it's the history of all humankind that's at risk here. It's the history of the peoples of the Middle East, it's the history of the Arab peoples, it would be the pre-history of the state that's trying to form itself in that area. It's to understand where people came from, how they developed into who they were, what are the major key advances, when did they occur and how we got to be who we are. So, Palmyra has material bearing on all of those questions. The antiquities of the past are important, but so are the people living there today and our major concern should be for the living," Dr Bourke says. "Though the living are the ones who are going to need evidence of the past when they start rebuilding their country."
Dr Bourke said archaeologists both within Syria and internationally have been risking their lives to protect Syrian antiquities by keeping an eye on international markets for any stolen items.
Classroom Activities
Here you can download worksheet, PowerPoints and other documents that we have used in class during this unit.
|
|
| ||||||
Unit 1 Review Materials
Click on the files below to download useful review materials
|
The following PowerPoint examines the impact of the Neolithic Revolution and the positives and negatives of civilization.
|
This review sheet describes some common characteristics among early civilizations and also explains their significance.
|
Completing CCOT charts will help you understand change and continuity though time.
| ||||||
| |||
