4.4 Pricing
What we will study?
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Analyse different pricing strategies: cost-based,competition-based, market-based
- Analyse the appropriateness of different pricing strategies
- Evaluate the impact of changes in conditions of supply and demand
- Calculate and interpret price, income, cross and advertising elasticity of demand
- Explain the relationship between elasticity and the product life cycle
- Analyse the relationship between elasticity and sales revenue
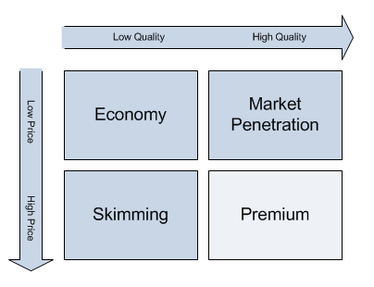
Pricing strategies
Pricing strategies - Cost-based (Cost-plus), Competition-based (price leadership), Market-based / Demand-based (Penetration and Skimming)
COST-BASED STRATEGIES:
Cost-plus pricing/ Mark-up pricing
- add a percentage/predetermined amount of profit (aka profit margin/mark-up) to average cost of production (Fixed + Variable Costs)
- floor pricing: low price = low profit margins by selling large volumes (economy brands)
- advantages: easy to calculate; disadvantages: requires intuitive decision-making
COMPETITION-BASED STRATEGIES:
Price leadership
- used for best-selling products/brands; no substitute product so business can decide price
- competitors establish their price based on selling price of the market/price leader
MARKET-LED STRATEGIES:
Penetration
- low price to gain market share, brand awareness
- slowly increase in price as product is more established
- used for mass market products, new products entering a well-established market
- drawbacks: low price may cause product to appear of a low quality
Skimming
- high price used to regain high costs of R&D, maximize profits
- slowly decrease in price as competitors are introduced
- used for innovative products, technologic products
- prestige pricing: permanently high price
- advantages: image of prestige; disadvantages: must be accompanied by effective marketing strategies
The appropriateness of a pricing strategy is dependent on branding/marketing objectives, promotional strategies, points of sale available, features of the product, costs of production, level of competition, and profit goals of the business.
Cost-plus pricing/ Mark-up pricing
- add a percentage/predetermined amount of profit (aka profit margin/mark-up) to average cost of production (Fixed + Variable Costs)
- floor pricing: low price = low profit margins by selling large volumes (economy brands)
- advantages: easy to calculate; disadvantages: requires intuitive decision-making
COMPETITION-BASED STRATEGIES:
Price leadership
- used for best-selling products/brands; no substitute product so business can decide price
- competitors establish their price based on selling price of the market/price leader
MARKET-LED STRATEGIES:
Penetration
- low price to gain market share, brand awareness
- slowly increase in price as product is more established
- used for mass market products, new products entering a well-established market
- drawbacks: low price may cause product to appear of a low quality
Skimming
- high price used to regain high costs of R&D, maximize profits
- slowly decrease in price as competitors are introduced
- used for innovative products, technologic products
- prestige pricing: permanently high price
- advantages: image of prestige; disadvantages: must be accompanied by effective marketing strategies
The appropriateness of a pricing strategy is dependent on branding/marketing objectives, promotional strategies, points of sale available, features of the product, costs of production, level of competition, and profit goals of the business.
What strategy?
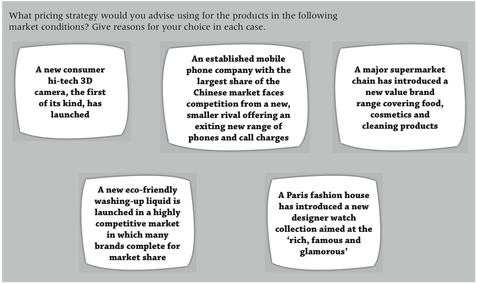
Which of the following strategies would you apply?
- Price skimming
- Predatory pricing
- Penetration or cost-plus pricing
- Penetration or price leadership
- Prestige / Value pricing
- Price skimming
- Predatory pricing
- Penetration or cost-plus pricing
- Penetration or price leadership
- Prestige / Value pricing
The importance of pricing
The importance of getting the pricing decision correct cannot be underestimated. If you get it wrong much hard work in market research and product development can be put at risk. Obviously PRICE is the amount paid by the consumer for the product and has a big influence on consumer demand for a product. DONT MAKE THE ASSUMPTION THAT CHEAPER MEANS A HIGHER DEMAND. If you were asked by your parents to go the convenience store to buy some soap, would you buy some that was being sold for 10yen? The answer, probably not. Why? Well I imagine that you might expect the quality to be poor and therefore it would not be a desirable product.
The 'Truth About Supermarkets' is an excellent introduction to the pricing strategies that firms can use. It will also give you some examples of less than ethical marketing practices. HIGHLY RECOMMENDED! http://www.bbc.com/news/uk-16027733
The 'Truth About Supermarkets' is an excellent introduction to the pricing strategies that firms can use. It will also give you some examples of less than ethical marketing practices. HIGHLY RECOMMENDED! http://www.bbc.com/news/uk-16027733
How to price a new product
The effects of lowering prices
|
Lowering prices can obviously increase sales as consumers are attracted to the possibility of finding a bargain. However, negative effects can also occur (in the case in the video on the right) and also if competing firms engage in a 'price-war'. This can be wonderful for the customer but, for the firms embroiled in the price war it can be very bad.
|
However, if your local supermarket is offering milk or bread at a 50% discount is very probably that the prices of their other products have actually increased. As seen in the video on the left from Australia. Finally check out this short article from the Economist. |
Price elasticity explained
If in doubt watch this...
Textbook review

1. Define the following terms: brand awareness, brand development, brand loyalty. (p206-207)
(6 marks)
2. In an extended response identify four major pricing strategies. Clearly explain how each strategy works by using a practical example. Some of these practical examples should include numerical examples. (p210-212)
(9 marks)
(6 marks)
2. In an extended response identify four major pricing strategies. Clearly explain how each strategy works by using a practical example. Some of these practical examples should include numerical examples. (p210-212)
(9 marks)
