04 Resources and the environment

During this unit we will study the following content:
- How human activity pollutes the environment
- How we can conserve energy
- The difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources
- Explain how humans can have a negative impact on the environment through industrial activity.
- Classify different types of pollution and their effects
- Explain the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources
Why is it an issue if we run out of oil?
|
|
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline.
Optimistic estimations of peak production forecast the global decline will begin by 2020 or later, and assume major investments in alternatives will occur before a crisis, without requiring major changes in the lifestyle of heavily oil-consuming nations.
Pessimistic predictions of future oil production operate on the theory that either the peak has already occurred, we are on the cusp of the peak, or that it will occur shortly and, as proactive mitigation may no longer be an option, predict a global depression, perhaps even initiating a chain reaction of the various feedback mechanisms in the global market which might stimulate a collapse of global industrial civilization, potentially leading to large population declines within a short period.
An Analogy of Peak Oil:
Optimistic estimations of peak production forecast the global decline will begin by 2020 or later, and assume major investments in alternatives will occur before a crisis, without requiring major changes in the lifestyle of heavily oil-consuming nations.
Pessimistic predictions of future oil production operate on the theory that either the peak has already occurred, we are on the cusp of the peak, or that it will occur shortly and, as proactive mitigation may no longer be an option, predict a global depression, perhaps even initiating a chain reaction of the various feedback mechanisms in the global market which might stimulate a collapse of global industrial civilization, potentially leading to large population declines within a short period.
An Analogy of Peak Oil:
- You like to go fishing in a pond
- The first day you catch one fish, the second you catch two fish, the third three fish.
- You become a better fisherman everyday.
- You catch more and more fish.
- But at some point the fish in the pond start running out.
- You cannot continue to catch 20 fish if there are not 20 fish left in the pond.
Chemical explosion, Barcelona 02/12/15 |
Drax Powerstation |
|
|
|
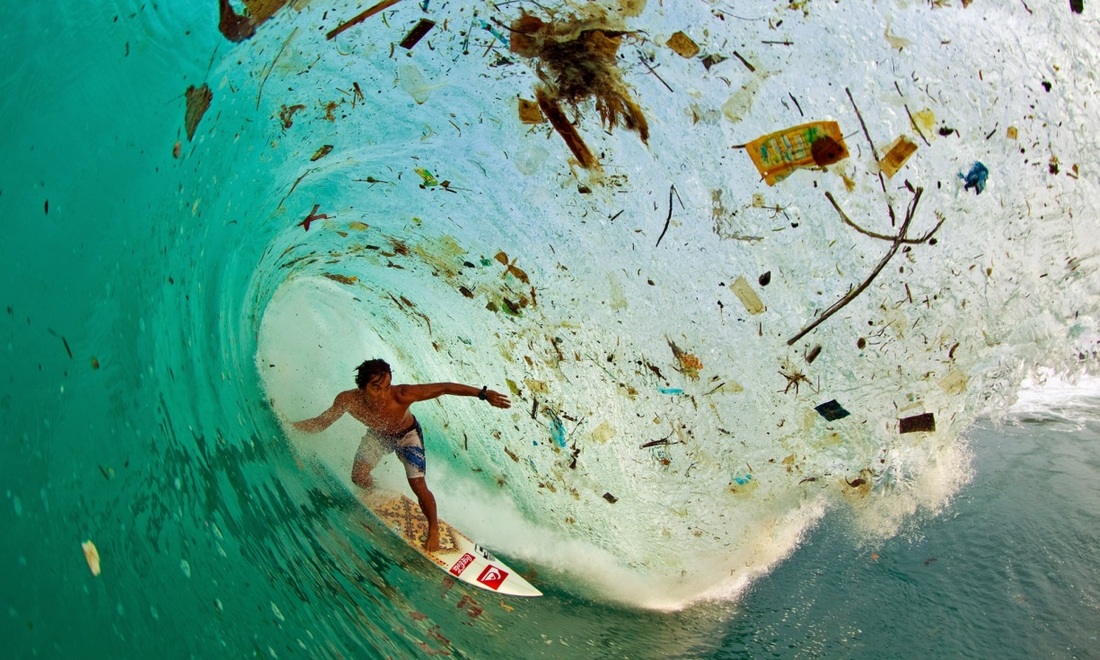
Pollution and waste
MEDCs have higher levels of consumption, so many produce more waste than LEDCs. The USA produces over 700 kg of waste per person per year. In LEDCs the figure is around 150 kg per person per year. This difference is due to different levels of consumption; it is also more common to reuse items in LEDCs.
As a country becomes more wealthy, the demand for consumer items increases. This means that items are replaced more frequently - leading to larger quantities of waste. For example, mobile phones and computers that still work may be discarded for a newer version.
In LEDCs waste production is lower because:
As a country becomes more wealthy, the demand for consumer items increases. This means that items are replaced more frequently - leading to larger quantities of waste. For example, mobile phones and computers that still work may be discarded for a newer version.
In LEDCs waste production is lower because:
- Less is bought because people are typically on lower incomes
- Less packaging is used on products
- Disposable items (eg razors, plastic plates and nappies) are used less
- Lower literacy levels means there is less production of written material