Imperialism and Nationalism
During this unit we will study the following:
- Industrial revolution and its dramatic impacts on the world
- Forces that contributed to imperialism and nationalism
- Various forms of colonial control
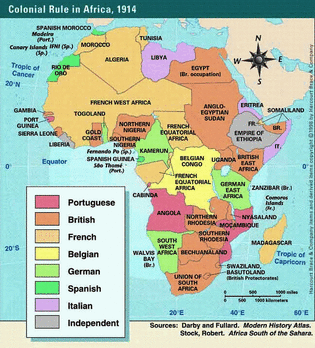
- Imperialism in Africa and Asia and how it still affects the world today
- The reactions of regions of the world to Western economic domination
- Analyze primary and secondary sources
- Explain the positive and negative results of imperialism and nationalism
- Write an analytical essay about the arguments for and against imperialism
Unit 7 Plan
TYPES OF IMPERIALISM
Europeans began building their empires in the western hemisphere in the early 1500s, but by the 1800s, Spain and Portugal were no longer powerful countries, and the largest British colony had become the United States. Britain, France, Germany, Russia, and the Netherlands continued to colonize during this era, but they also devised other ways to spread their empires. In the late 19th century Japan and the United States joined the European nations as an imperialist power.
Types of imperialism in the 1800s included:
*these can co-exist together; an imperial power would not necessarily only use one method of imperialism.
Europeans began building their empires in the western hemisphere in the early 1500s, but by the 1800s, Spain and Portugal were no longer powerful countries, and the largest British colony had become the United States. Britain, France, Germany, Russia, and the Netherlands continued to colonize during this era, but they also devised other ways to spread their empires. In the late 19th century Japan and the United States joined the European nations as an imperialist power.
Types of imperialism in the 1800s included:
- Colonial imperialism - This form of imperialism is virtual complete takeover of an area, with domination in all areas: economic, political, and socio-cultural. The subjugated area existed to benefit the imperialist power, and had almost no independence of action. In this era, almost all of Africa and southern and southeast Asia were colonized.
- Economic imperialism - This form of imperialism allowed the area to operate as its own nation, but the imperialist nation almost completely controlled its trade and other business. For example, it may impose regulations that forbid trade with other nations, or imperialist companies may own or have exclusive rights to its natural resources. During this era, China and most of Latin America were subjected to economic imperialism.
- Political imperialism - Although a country may have had its own government with natives in top political positions, it operated as the imperialist country told it to. The government was sometimes a relatively permanent "puppet government," as happened in late Qing China, and other times the control was temporary, as occurred in the Dominican Republic when the United States ran its government until it got out of debt.
- Socio-cultural imperialism - The dominating country deliberately tried to change customs, religions and languages in some of the countries. A good example was British India, where English was taught in schools, Indian soldiers dressed British-style, and western trading rules were set up. Generally, the imperialist countries assumed their cultures to be superior, and often times they saw themselves as bringing about improvements in the society.
*these can co-exist together; an imperial power would not necessarily only use one method of imperialism.
Empire: How Britain made the modern world
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Motives for Imperialism
The empire-building undertaken by Western Europe in this era is essential to understanding how events in the modern era played out. The long-term effects of imperialism are still seen in the world today. For this reason, it is essential that students understand what imperialism was, how nations built empires, how nations governed their empires, and the structures of these empires.
a) POLITICAL MOTIVATIONS:
As nation-states competed for power, they sought new ways to compete and show dominance over each other
b) ECONOMIC MOTIVATIONS:
Industrialization led to a need for greater raw materials and new markets
c) CULTURAL / SOCIAL MOTIVATIONS:
Justified by Social Darwinism (adapted from survival of the fittest and natural selection)
Geopolitics is the study of how geography affects political decisions / policy.
E.g. Policies and decisions are often based on the recognition that certain areas of the world are valuable for political / strategic reasons
i) Allowed Europeans to break the barriers preventing them from conquering the interiors of Africa and Asia
ii) Advances in health care prevented malaria and tropical diseases; steam ships allowed Europeans to sail up formerly unnavigable rivers
a) POLITICAL MOTIVATIONS:
As nation-states competed for power, they sought new ways to compete and show dominance over each other
b) ECONOMIC MOTIVATIONS:
Industrialization led to a need for greater raw materials and new markets
c) CULTURAL / SOCIAL MOTIVATIONS:
Justified by Social Darwinism (adapted from survival of the fittest and natural selection)
- Europeans deserved to conquer Africa and Asia because they were better
- Fear of nation becoming “extinct” because it failed to adapt to the world where other countries were acquiring colonies
Geopolitics is the study of how geography affects political decisions / policy.
E.g. Policies and decisions are often based on the recognition that certain areas of the world are valuable for political / strategic reasons
- Egypt was important for Britain to protect the Suez Canal as was S.Africa as a trading post to India.
- USA control of Panama to protect the Panama Canal
i) Allowed Europeans to break the barriers preventing them from conquering the interiors of Africa and Asia
ii) Advances in health care prevented malaria and tropical diseases; steam ships allowed Europeans to sail up formerly unnavigable rivers
Direct rule vs indirect rule
19th Century Imperialism
Pros and Cons of Imperialism
The term imperialism has a negative sound to it, as it means a forceful or covert expansion into unwilling territories. However, it has also ushered many smaller countries onto the path of development. Following are the pros and cons of imperialism:
Pros
Imperialism has its own positive aspects, but in the longer run when greed takes over the reason for helping another nation, it leads to destruction of a nation, and generations to come are severely impacted by the actions of few.
Pros
- Most superpowers brought with them modern technologies and introduced industrialization in smaller nations, boosting the economy.
- Introduced the concept of a democratically elected popular government to ensure political stability.
- Education and scientific thinking was introduced and encouraged..
- Better health care facilities were provided.
- New transportation systems such as rail, road sea and air were introduced.
- New languages, religions and a new way of life were introduced.
- The imperialists countries gained cheap, efficient workforce.
- Food production increased due to better farming methods.
- Nations that resisted growth or expansions in their territory led to widespread genocide and ethnic cleansing.
- Obtaining valuable natural resources became a bone of contention between the developed countries, resulting in political foul play.
- New religions were forced upon and native belief was discredited.
- Most traditional culture and languages were simply wiped away.
- Natural resources were exploited, without giving actual due.
- Labor was discriminated and forced into slavery, and had their basic rights taken away.
- Many Asians and Africans were shipped to America and England, against their will as cheap labour.
Imperialism has its own positive aspects, but in the longer run when greed takes over the reason for helping another nation, it leads to destruction of a nation, and generations to come are severely impacted by the actions of few.
