Unit 1.1: Introduction to Business Management
What we will study?
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Explain the role of organizations in combining human, physical and financial resources to create a product.
- Understand the main business functions: human resources, finance and accounts, marketing and operations.
- Explain the nature of business activity in the primary, secondary, tertiaryand quaternary sectors.
- Examine the role of entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship in business activity.
- Identify the reasons for starting a business, the common steps involved and likely problems a new business may face.
- Analyse the elements of a business plan
What is a business?
A business is any organisation that makes goods or provides services. These range from small firms owned and run by just one self employed person, through to large companies which employ thousands of staff all over the world. Businesses exist to provide goods or services that satisfy a consumers' needs or wants, usually with the aim of making a profit . Goods are physical products - such as burgers or cars and can be classified as either consumer goods Services are non-physical products such as hotel accommodation, insurance services or internet service providers.
- Consumer goods (durable) = washing machines, cars, televisions.
- Consumer goods (non-durable) = food, drinks and sweets that can only be used once.
- Consumer services = hairdressing, train journeys.
- Capital goods = physical goods that are used in industry to make other goods and services, such as machines or if you are a hairdresser, a pair of scissors.
Business objectives
All businesses have objectives or aims to achieve. Their objectives may vary depending on the type of business and the situation the business is in. The most common objectives are:
- Profit: Profit is what keeps a company going and is the main objective of most businesses. Normally a business will try to obtain a satisfactory level of profits so they do not have to work long hours to pay too much tax.
- Increase added value: Value added is the difference between the price and material costs of a product. E.g.: If the price when selling a pen is $3 and it costs $1 in material, the value added would be $2. However, this does not take in account overheads and taxes. Added value could be increased by working on products so that they become more expensive finished products. One easy example of this is a mobile phone with a camera would sell for much more than one without it. Of course, you will need to pay for the extra camera but as long as prices rise more than costs, you get more profit.
- Growth: Growth can only be achieved when customers are satisfied with a business. When businesses grow they create more jobs and make them more secure when a business is larger. The status and salary of managers are increased. Growth also means that a business is able to spread risks by moving to other markets, or it is gaining a larger market share. Bigger businesses also gain cost advantages, called economies of scale.
- Survival: If a business does not survive, its owners lose everything. Therefore, businesses need to focus on his objective the most when they are: starting up, competing with other businesses, or in an economic recession.
- Service to the community: This is the primary goal for most government owned businesses. They plan to produce essential products to everybody who need them.
Business activity / Factors of production

Investopedia explains 'Factors Of Production'
In essence, land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship encompass all of the inputs needed to produce a good or service. Land represents all natural resources, such as timber and gold, used in the production of a good. Labor is all of the work that laborers and workers perform at all levels of an organization, except for the entrepreneur. The entrepreneur is the individual who takes an idea and attempts to make an economic profit from it by combining all other factors of production. The entrepreneur also takes on all of the risks and rewards of the business. The capital is all of the tools and machinery used to produce a good or service.
In essence, land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship encompass all of the inputs needed to produce a good or service. Land represents all natural resources, such as timber and gold, used in the production of a good. Labor is all of the work that laborers and workers perform at all levels of an organization, except for the entrepreneur. The entrepreneur is the individual who takes an idea and attempts to make an economic profit from it by combining all other factors of production. The entrepreneur also takes on all of the risks and rewards of the business. The capital is all of the tools and machinery used to produce a good or service.
Business functions
Once a business has been properly established and has taken on a reasonable number of employees, the organisational structure will involve the business being splits into number of different departments, each of which has a specific job or task to do - these are called 'functions'.
The main functional areas of a business are outlined briefly below:
The main functional areas of a business are outlined briefly below:
The growth of firms and Economies of scale

Reasons why firms may wish to grow in size
- To diversify and spread risk
- To take advantage of higher levels of demand that exist
- To tap into emerging markets
- To take advantage of changing market conditions
- To take advantage of economies of scale
- To take advantage of globalisation and expand into overseas markets
- To increase market share and develop greater monopoly power
|
Type of Merger
Horizontal Merger Vertical Merger |
Potential benefits to the firm
|
|
Type of Economies of Scale
Financial Economies of Scale Purchasing Economies of Scale Technical Economies of Scale Managerial Economies of Scale Risk Bearing Economies of Scale |
Explanation
|
What is an entrepreneur?
|
STARTING A BUSINESS: ROLE OF THE ENTREPRENEUR
An entrepreneur is someone who takes the financial risk (and reaps the rewards!) of starting and managing a new venture. These people have:
|
QUALITIES OF THE ENTREPRENEUR:
|
ARE YOU AN ENTREPRENEUR? CLICK HERE
|
PROBLEMS FACED BY START-UPS
Even if an entrepreneur has all of the right qualities, success with a new business can never be guaranteed. Many businesses fail during the first year of operation, because of:
CLICK HERE FOR A STARTING YOUR OWN BUSINESS QUIZ |
What is an intrapreneur?An intrapreneur takes an existing idea or develops a new one, and through all of the obstacles that exist, drive it forward.
|
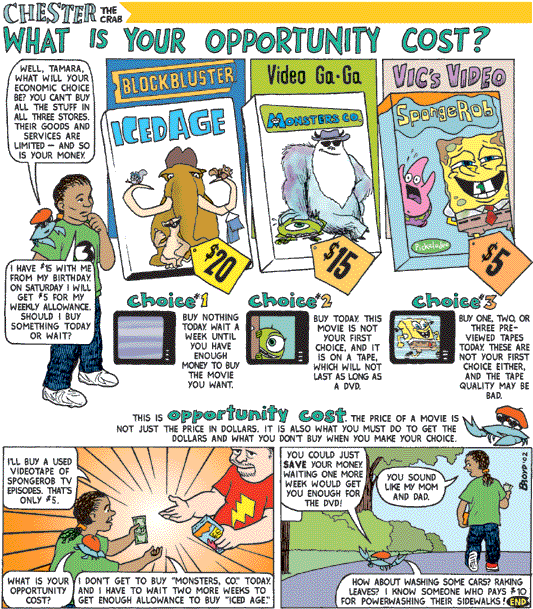
Opportunity cost
In 1936 the German Nazi leader Hermann Goering said “We have no butter…but I ask you, would you rather have butter or guns…preparedness makes us powerful. Butter merely makes us fat.” The important word of course is or. Goering suggested that Germany had a choice guns or butter. Opportunity cost - is the benefit that is lost in making a choice.
Examples
* Coca Cola decide to spend $50 billion on advertising
* The government decides to spend $100 billion on hospitals
* An individual allocates their time to study rather than playing football
Examples
* Coca Cola decide to spend $50 billion on advertising
* The government decides to spend $100 billion on hospitals
* An individual allocates their time to study rather than playing football
|
DEFINITION of 'Capital Goods'
1. Any tangible assets that an organization uses to produce goods or services such as office buildings, equipment and machinery. Consumer goods are the end result of this production process. Read more: Capital Goods Definition | Investopedia http://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/capitalgoods.asp#ixzz3k4Z6GWKQ |
|