Stone Age - Neolithic Revolution - Early Civilizations
At the beginning of the unit we will study the transition from hunter gathering societies to sedentary agriculture and the subsequent birth of 'civilizations'. The following PowerPoint will provide you with a review of the major ideas you need to know and should be used in conjunction with your assigned reading.
Characteristics of Early Agricultural Civilizations
It is imperative that you know and understand the common characteristics of early agricultural civilizations. Note that the characteristics mentioned below expand on the definition of a civilization.
|
Characteristic
Permanent settlements Specialized workers Technological innovations Governments Social Classes Religion |
Significance
As people began to farm, they began to settle in one place. Eventually, villages, towns, and cities developed. Important examples of early permanent settlements are Catal Huyuk and Jericho. Early cities became the focus of a civilization because of their political, cultural, and economic importance As farming produced food surpluses, many people did not have to farm and were able to specialize in other areas, such as ceramics and textile production. As civilizations advanced, people were able to specialize in other professions, such as commerce, civil engineers, religious leaders, and political leaders Early agricultural/Neolithic civilizations developed the use of various metals (copper, gold, and bronze in that order) for items such as weapons and other luxury goods; other examples of technological innovations, largely due to the specialization of workers, include advanced irrigation apparatus, the wheel, weapons, sundials, etc. As cities developed in the early civilizations, the inhabitants required large public works projects beyond the scope of private citizens. As a result, governments formed to organize and oversee the fabrication of roads, irrigation projects, public buildings, etc. and to regulate commerce (through the establishment of laws, courts, and a system of punishment. Moreover, governments functioned to protect citizens from invasions and to organize attacks on rival civilizations. Governments also collected taxes from the city dwellers As people settled on land to farm, there were those who laid claim to more land than others, thus forming the first elite social classes. Early civilizations had an elite social class comprised of large land-owners. Many civilizations, such as Sumer, had a slave class, although in most cases slaves could buy their freedom. Likewise, men could sell women and children into slavery to pay off debts. As people began to observe more closely their environment in an effort to increase agricultural productivity, knowledge of seasons and nature increased. Attempting to explain natural processes and natural disasters, people developed elaborate stories about the origin of life and rituals to appease gods they perceived as controlling nature. Over time, a group of specialized workers emerged to lead these rituals and devote their lives to the worship of deities. |
Comparing Early River Civilizations
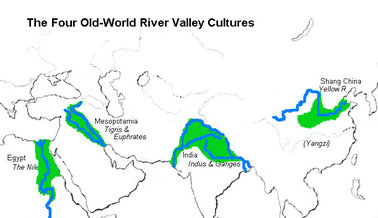
A surplus of agricultural production led to the rise of complex human societies, or civilizations. With the need of agricultural societies to irrigate, it is not surprising that many civilizations emerged in river valleys. The River Valley civilizations that emerged on the Yellow River (China), the Indus River (India), the Nile River (Egypt), and between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers (Mesopotamia) made lasting contributions to civilizations. The following chart compares the important features of a few of these river valley civilizations. As you look over this file, attempt to piece together what these civilizations have in common and what differentiates them.
*Please note that Mesmoamerican Classical Civilizations will be studied in Unit II
|
| ||||
Analyzing Why??
In the AP Exam you will have to answer a Comparative FRQ. In order to achieve a high score for this question you must be able to identify similarities and differences between different civilization but also WHY they were similar or different. Using the notes below as a guide think of your own ideas of how and why Classical Civilizations were similar / different. Those noted below are by no means the only similarities and differences. Think about their Belief Systems, Trading Networks, Interactions with their Environments.
Comparing Social Structures
Slavery
In Greece and Rome slavery was widely practiced.
Why? = Slaves were from foreign conquest.
China had slavery but it was not widely practiced.
Why? = China was not particularly expansionistic.
India didn't really have slavery?
Why? = It didn't need the because of the caste-system
Comparing the Role of Women
In Greece, Rome, India and China were all patriarchal societies although women in Sparta had more freedom than most.
Why?
o China = Confucianism decreed that women must obey their husbands.
o India = Caste system and the increasing decline of women during the Gupta empire. Under Hindu law women were subservient to men, they were not allowed allowed to own or inherit property.
o Rome = Rome had the paterfamilias (a law which recognized the dominant role of men over women) which was similar to Confucian ideas on gender.
o Greece = women in Sparta had more freedom that women in Athens as while their husbands and sons were training and fighting in battle they were needed to work.
Social Pyramids
India had the Caste System.
Why? = Aryans introduced it to control the native population.
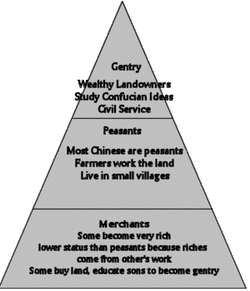
China’s social pyramid is based on Confucianism which meant that merchants considered ‘lower’ than peasants.
Why? = The Han favored Confucianism as it re-enforced their position.
Political Organization
Greece and Rome were Expressionistic.
o Why? = they were both ethnocentric, lack of resources.
China was not expansionistic
o Why? = Thought they were the centre of the earth (Middle Kingdom), blocked in by natural barriers so they were isolated. More concerned with keeping invaders out (Great Wall)
Centralized or decentralized?
Greece and India were de-centralized.
o Why? = Geographic barriers made centralization very difficult. Led to rival city-states in Greece and made centralization in India impossible due its large size.
Culture
Greece and China valued educational achievement. This meant an individual’s ability was more important than his wealth. E.g. the bureaucracy in China could contain peasants if they passed the civil service exam.
Comparing Social Structures
Slavery
In Greece and Rome slavery was widely practiced.
Why? = Slaves were from foreign conquest.
China had slavery but it was not widely practiced.
Why? = China was not particularly expansionistic.
India didn't really have slavery?
Why? = It didn't need the because of the caste-system
Comparing the Role of Women
In Greece, Rome, India and China were all patriarchal societies although women in Sparta had more freedom than most.
Why?
o China = Confucianism decreed that women must obey their husbands.
o India = Caste system and the increasing decline of women during the Gupta empire. Under Hindu law women were subservient to men, they were not allowed allowed to own or inherit property.
o Rome = Rome had the paterfamilias (a law which recognized the dominant role of men over women) which was similar to Confucian ideas on gender.
o Greece = women in Sparta had more freedom that women in Athens as while their husbands and sons were training and fighting in battle they were needed to work.
Social Pyramids
India had the Caste System.
Why? = Aryans introduced it to control the native population.
China’s social pyramid is based on Confucianism which meant that merchants considered ‘lower’ than peasants.
Why? = The Han favored Confucianism as it re-enforced their position.
Political Organization
Greece and Rome were Expressionistic.
o Why? = they were both ethnocentric, lack of resources.
China was not expansionistic
o Why? = Thought they were the centre of the earth (Middle Kingdom), blocked in by natural barriers so they were isolated. More concerned with keeping invaders out (Great Wall)
Centralized or decentralized?
Greece and India were de-centralized.
o Why? = Geographic barriers made centralization very difficult. Led to rival city-states in Greece and made centralization in India impossible due its large size.
Culture
Greece and China valued educational achievement. This meant an individual’s ability was more important than his wealth. E.g. the bureaucracy in China could contain peasants if they passed the civil service exam.
Unit 1 Review Materials
|
Analyze similarities and differences in methods of political control in two of the following empires in the Classical period.
|
Early Global Trade and Contact
|
Review MCQ for Unit 1
| ||||||
|
Completing CCOT charts will help you prepare for the CCOT Free Response Question on the Exam. Choose a world region, e.g. Europe and complete the chart as best you can. You'll be surprised at how much you know!!
|
Unit 1 Review Packet
| ||||
