Classical Rome
Classical Rome, Greece and China developed their own beliefs, lifestyles, political institutions, and social structures. However, there were important similarities among them:
Culture = shared practices (how they did things), beliefs / values, way of life, education, homes, diet.
Social = institutions and organizations created by people, groups/levels of people.
Political = methods of control, types of government.
As we move on to studying our second Classical Civilization (Rome) we will look at similarities and differences between it and Greece and attempt to explain them.
- Patriarchal family structures - Like the river valley civilizations that preceded them, the classical civilization valued male authority within families, as well as in most other areas of life.
- Agricultural-based economies - Despite more sophisticated and complex job specialization, the most common occupation in all areas was farming.
- Complex governments - Because they were so large, these three civilizations had to invent new ways to keep their lands together politically. Their governments were large and complex, although they each had unique ways of governing
- Expanding trade base - Their economic systems were complex. Although they generally operated independently, trade routes connected them by both land and sea.
Culture = shared practices (how they did things), beliefs / values, way of life, education, homes, diet.
Social = institutions and organizations created by people, groups/levels of people.
Political = methods of control, types of government.
As we move on to studying our second Classical Civilization (Rome) we will look at similarities and differences between it and Greece and attempt to explain them.
What we will study

- How the development of Rome was influenced by its geography?
- Its social structure and political systems
- Its cultural values (art, philosophy, belief systems)
- Its impact on modern the modern world
- Roman imperialism (direct / indirect)?
- What factors (internal or external) led to the downfall of the Roman Empire?
Sample Classroom Activities
In the document below are are examples of some classroom activities from the Classical Rome unit.
Republic or Empire?
The Pax Romana
Background
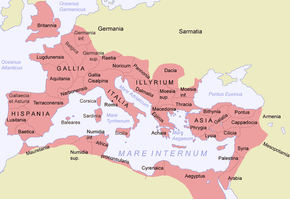
The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BCE. The government was run by elected officials called Senators, who were chosen from the upper class called Patricians. The lower class, Plebeians, made up the majority of the population and were generally farmers, artisans, and merchants.By 270 BCE, Rome controlled all of Italy. They also soon conquered Carthage, Macedonia, Greece, and parts of Asia Minor. This expansion led to civil war and the end of the Republic when Julius Caesar took power in 48 BCE. After his murder, Caesar's grandnephew, Augustus, became Emperor. This began a 200 year long peace called the Pax Romana. The Pax Romana became a time of cultural and intellectual achievements for Rome.
Law
Rome's greatest achievement was its system of laws. Some of the features of this system include, men being equal under the law, having the right to face their accusers, and being considered innocent until proven guilty. Later, these laws were written down and named the Laws of the Twelve Tables. Many aspects of this system of justice survive today in law codes around the world.
The Roman Republic was founded in 509 BCE. The government was run by elected officials called Senators, who were chosen from the upper class called Patricians. The lower class, Plebeians, made up the majority of the population and were generally farmers, artisans, and merchants.By 270 BCE, Rome controlled all of Italy. They also soon conquered Carthage, Macedonia, Greece, and parts of Asia Minor. This expansion led to civil war and the end of the Republic when Julius Caesar took power in 48 BCE. After his murder, Caesar's grandnephew, Augustus, became Emperor. This began a 200 year long peace called the Pax Romana. The Pax Romana became a time of cultural and intellectual achievements for Rome.
Law
Rome's greatest achievement was its system of laws. Some of the features of this system include, men being equal under the law, having the right to face their accusers, and being considered innocent until proven guilty. Later, these laws were written down and named the Laws of the Twelve Tables. Many aspects of this system of justice survive today in law codes around the world.
Engineering

The Romans built engineering marvels across their empire, such as roads, harbors, and bridges,. They were well known for the building of aqueducts, which were bridge like structures used to carry fresh water across long distances. In Segovia, Spain the Roman aqueduct still functions today.
Art & Architecture
Roman art and architecture is a blending of Greek and Roman elements. In art, Rome copied many Greek statues, but also produced a more realistic style ofportraiture art instead of the idealized forms favored by the Greeks. In architecture, Rome used Greek columns, but modified them to be more elaborate, as well as using the arch and dome quite extensively, something the Greeks did not do. An example of Roman use of arches and domes can be seen in the Pantheon
Art & Architecture
Roman art and architecture is a blending of Greek and Roman elements. In art, Rome copied many Greek statues, but also produced a more realistic style ofportraiture art instead of the idealized forms favored by the Greeks. In architecture, Rome used Greek columns, but modified them to be more elaborate, as well as using the arch and dome quite extensively, something the Greeks did not do. An example of Roman use of arches and domes can be seen in the Pantheon
Document Based Questions
|
| ||||
The Legacy of the Roman Empire
The legacy of the Romans is extremely important. Many things that form part of everyday life were introduced or improved by the Romans. Over the centuries since the collapse of the Roman Empire, Romans ideas, literature, art and architecture have influenced many people around the world.
The question 'what have the Romans ever done for us' was made famous by the film the Life of Brian. Even though the film was a comedy, the sketch from the film is extremely useful to us. It makes us appreciate how much the Romans did actually do!
Some examples of things that Romans introduced across their conquered territories that are still in use today:
The question 'what have the Romans ever done for us' was made famous by the film the Life of Brian. Even though the film was a comedy, the sketch from the film is extremely useful to us. It makes us appreciate how much the Romans did actually do!
Some examples of things that Romans introduced across their conquered territories that are still in use today:
The Fall of Rome
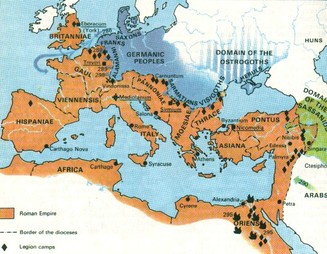
Rome ruled all around the Mediterranean and large sections of Europe and Southwest Asia. Yet in the end, the problems grew too great and the Western Roman Empire fell.
Why did the empire fall apart?
There is no one single reason, but was instead a series of problems that grew too large to solve.
One problem was that the empire grew too large to govern. The Romans tried to solve this by dividing the empire into the Eastern and Western Roman Empire.
Another problem was that the Roman men no longer wanted to serve in the army. The pay was not great. Sometimes the legion was not paid at all. Most men did not want to be away from their families and farms for long periods of time. The Romans tried to solve this by hiring barbarians to fight for them. In addition, the outer edges of the Empire were well defended but there was little defence with in the Empire. This meant that once barbarians had broken through there was nothing to stop them marching to Rome.
There were other problems. Civil wars broke out in Rome between different factions. The rich grew disinterested in helping Rome and only wanted more for themselves and their families. The population of Rome shrank. Trade decreased while taxes and prices increased. The poor were overtaxed. The use of slaves put people out of work. The roads fell into disrepair.
The Romans were aware of these problems and sometimes, under a good emperor, they would work on them for a while. In time, the good emperor would be gone and a bad one would take his place. Soon the problems in the Western Roman Empire grew so great that the Western (European) Roman empire, which included the city of Rome, fell to barbarian tribes in Europe.
The Eastern Roman empire continued another 1000 years.
Why did the empire fall apart?
There is no one single reason, but was instead a series of problems that grew too large to solve.
One problem was that the empire grew too large to govern. The Romans tried to solve this by dividing the empire into the Eastern and Western Roman Empire.
Another problem was that the Roman men no longer wanted to serve in the army. The pay was not great. Sometimes the legion was not paid at all. Most men did not want to be away from their families and farms for long periods of time. The Romans tried to solve this by hiring barbarians to fight for them. In addition, the outer edges of the Empire were well defended but there was little defence with in the Empire. This meant that once barbarians had broken through there was nothing to stop them marching to Rome.
There were other problems. Civil wars broke out in Rome between different factions. The rich grew disinterested in helping Rome and only wanted more for themselves and their families. The population of Rome shrank. Trade decreased while taxes and prices increased. The poor were overtaxed. The use of slaves put people out of work. The roads fell into disrepair.
The Romans were aware of these problems and sometimes, under a good emperor, they would work on them for a while. In time, the good emperor would be gone and a bad one would take his place. Soon the problems in the Western Roman Empire grew so great that the Western (European) Roman empire, which included the city of Rome, fell to barbarian tribes in Europe.
The Eastern Roman empire continued another 1000 years.
Review Materials
|
|
