1.2 Elasticities
What we will study?
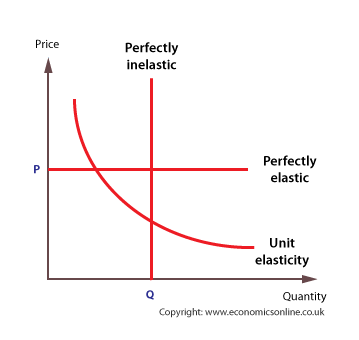
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
CROSS-PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
INCOME ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY
- What is price elasticity of demand?
- Calculating price elasticity of demand
- Interpreting the value of price elasticity of demand
- PED changes at different points on the demand curve
- Determinants of price elasticity of demand
- Price elasticity of demand and total revenue
- Price elasticity of demand and sales taxes
CROSS-PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
- Calculating cross-price elasticity of demand (XED)
- Interpreting XED values
- Applications of XED
INCOME ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
- Calculating income elasticity of demand (YED)
- Interpreting YED values
- YED and industry expansion
- YED and sectors of the economy
- YED and the business cycle
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY
- Calculating price elasticity of supply (PES)
- Interpreting PES values
- Determinants of PES
- Applications of PES
Introduction to Elasticities
Elasticity is an economic concept which refers to the responsiveness among consumers or producers to a change in a variable which affects either the market demand or the market supply.
There are four types of elasticity that we will study in this unit:
• Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in the good’s price.
• Cross-price elasticity of Demand (XED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of one good to a change in the price of a related goo (either a substitute or a complement).
• Income Elascity of Demand (YED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in their income.
• Price elasticity of Supply (PES): Measures the responsiveness of producers of a particular good to a change in the price of that good.
There are four types of elasticity that we will study in this unit:
• Price Elasticity of Demand (PED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in the good’s price.
• Cross-price elasticity of Demand (XED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of one good to a change in the price of a related goo (either a substitute or a complement).
• Income Elascity of Demand (YED): Measures the responsiveness of consumers of a particular good to a change in their income.
• Price elasticity of Supply (PES): Measures the responsiveness of producers of a particular good to a change in the price of that good.
Price Elasticity of Demand |
Cross Elasticity of Demand |
Income Elasticity of Demand |
Price Elasticity of Supply |
