01 The Foundations of Economics
What we will study?
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Understand the economic concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost and utility.
- Explain the Factors of Production.
- Explain the nature of business activity in the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary sectors.
- Interpret and construct production possibility curves.
- Differentiate between micro / macro economics and positive / normative economics.
- Evaluate the (+/-'s) of planned versus free market economies .
- Use "development" terminology, e.g LEDC, NIC, MEDC and be able to evaluate the (+/-'s) of the Human Development Index.
Crash Course Economics
Scarcity: Resources are scarce whilst human wants are unlimited
This is the reason for the existence of this subject. In reality most resources are scarce. Similarly individuals and nations have unlimited wants.
|
Scarce Resources
THE BASIC ECONOMIC PROBLEM – the problem arises because resources are scarce, but human wants are unlimited. |
|
The Factors of Production
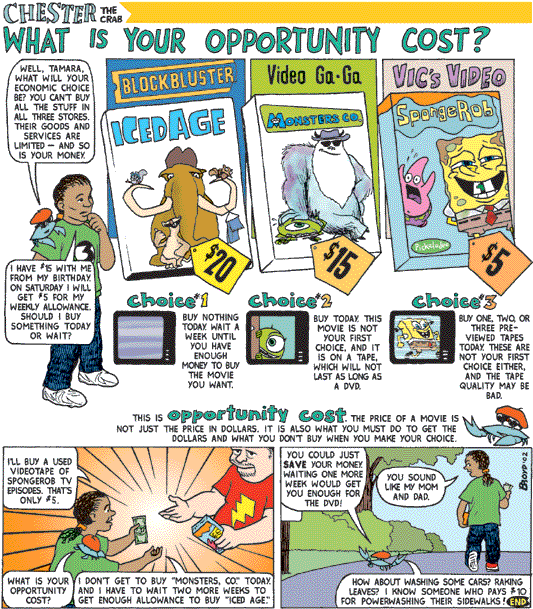
Opportunity Cost
In 1936 the German Nazi leader Hermann Goering said “We have no
butter…but I ask you, would you rather have butter or guns…preparedness makes us powerful. Butter merely makes us fat.” The important word of course is or. Goering suggests that Germany has a choice – guns or butter. Economic choice - is deciding between different uses of scarce resources Opportunity cost - is the benefit that is lost in making a choice between two competing uses of scarce resources. It is the next best alternative |
|
Examples of Opportunity Cost
This is about how resources are allocated between competing uses Examples * Coca Cola decide to spend $50 billion on advertising * The government decides to spend $100 billion on hospitals * An individual allocates their time to study rather than playing football ACTION 1. Think of an opportunity cost that you have experienced recently a) with money b) with your time 2. What could be an opportunity cost of you staying up late studying for a test? Answer: The next day you will feel tired and sleepy so therefore your opportunity cost is a good nights sleep. |
|
The Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost
|
Why does the PPC bow outwards?
The production possibility curve (PPC) is a model showing how resources can be used to produce two different goods or services. In the video on the left we have Pizzas and Cars. The graph is bowed outwards due to a basic concept used in economics - the principle of increasing opportunity cost. If a producer were to produce more of one good or service, the scarcity of resources dictates that it is impossible to maintain the previous amount of production of the other good or service. If more of one good or service is produced, the opportunity cost of the reduction of the other good or service increases, therefore the gradient of the curve increases. In this case it would mean that resources such as pizza makers are now working in car factories and obviously they arent going to be as productive as skilled car factory workers because they are more suited to making pizzas. |
|
Utility |
Micro and macroeconomics |
|
|
|
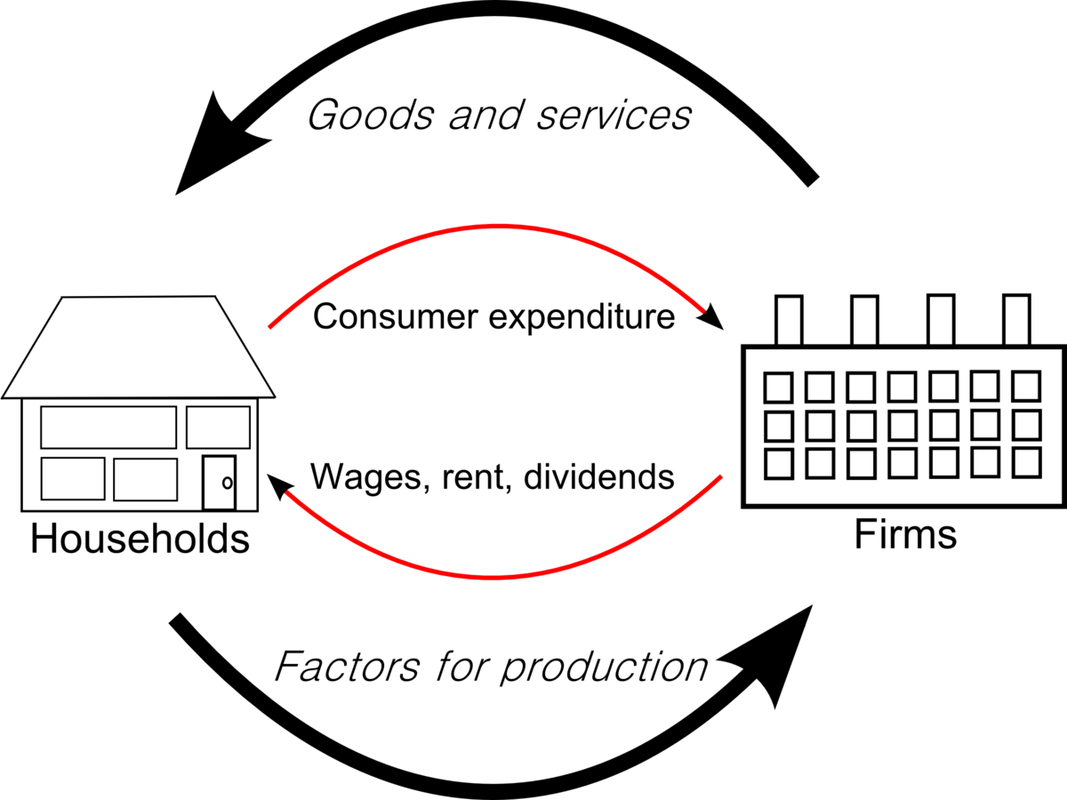
The Circular Flow of Income
Economic Systems: Free Market vs Command vs Mixed |
Milton Freeman on the Free Market System vs. The Command Economy |