4.3 Product
What we will study?
By the end of this unit you should be able to:
- Classify products by line, range and mix
- Describe the importance of new product design and development
- Analyse the stages of a typical product life cycle
- Analyse the relationship between the product life cycle and the marketing mix, profitand cash flow
- Understand product portfolio analysis and the application of the Boston Consulting Group Matrix
- Discuss the importance and role of branding
- Use the Boston matrix to develop future strategic direction
- Distinguish between different types of branding
"It is not the employer who pays wages. He only handles the money. It is the product that pays the wages and it is the management that arranges the production so that the product may pay the wages."
- Henry Ford
Classification of products
Product line
A product line refers to a variety of the same product that a business produces for customers of a particular market. They usually differ in size, colour, price or quality so that there is a greater chance that it meets the needs of different customers.
A product line refers to a variety of the same product that a business produces for customers of a particular market. They usually differ in size, colour, price or quality so that there is a greater chance that it meets the needs of different customers.
Product mix
A product mix, also known as the product assortment, refers to the variety of the different product lines that business produces. By having a wide product mix, sometimes referred to as the product portfolio, business should be able to increase overall sales as a variety of products are sold to a larger customer base
A product mix, also known as the product assortment, refers to the variety of the different product lines that business produces. By having a wide product mix, sometimes referred to as the product portfolio, business should be able to increase overall sales as a variety of products are sold to a larger customer base
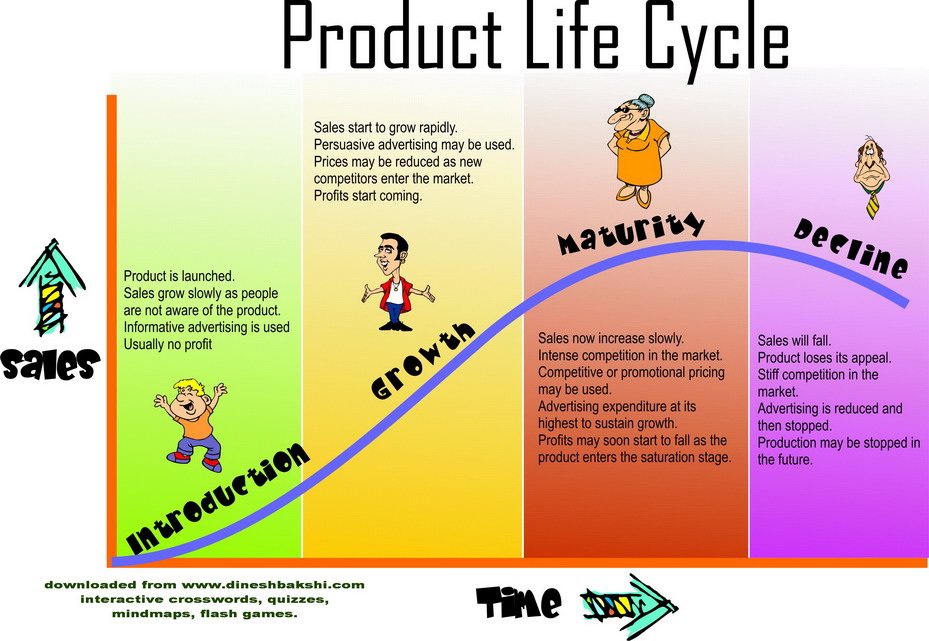
Product life cycle
The "Product Life Cycle" shows the different stages that a product is likely to go through from its initial design and launch to its eventual decline and withdrawal from the market.
There are generally six stages in a product's life cycle:
There are generally six stages in a product's life cycle:
- Research & development (R&D)
- Launch (introduction of the product)
- Growth
- Maturity
- Saturation
- Decline
Read this......
|
| ||||
|
How can a business extend the life cycle of a product?
Take a look at how the product life cycle of Lucozade has evolved. When I grew up watching John Barnes (when football was good) Lucozade, as it is today was a sports drink. Like Gatorade, but better. The marketing department at Lucozade have done an excellent job in reinventing the product over the years. |
Analyse the relationship between the product life cycle and the marketing mix, and determine appropriate extension strategies.
|
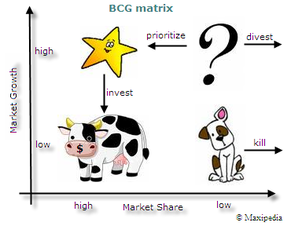
Product portfolio analysis - The Boston Matrix
This is an analysis of elements of a company's product mix to determine the optimum allocation of its resources. The two most common measures used in a portfolio analysis are market growth rate and relative market share.
Textbook review

1. In an extended response identify the 6 major steps in the
development process for a product. Clearly explain the meaning of each
step. (p199-200)
(15 marks)
2. Draw a diagram for the product life cycle. Clearly label all parts of the diagram.
Also show on the diagram the implementation of an extension strategy. (p201-202)
(5 marks)
3. Draw the BCG Matrix clearly labelling all features on the diagram? (p204-205)
(5 marks)
(15 marks)
2. Draw a diagram for the product life cycle. Clearly label all parts of the diagram.
Also show on the diagram the implementation of an extension strategy. (p201-202)
(5 marks)
3. Draw the BCG Matrix clearly labelling all features on the diagram? (p204-205)
(5 marks)