Unit III - Financial Capability

This unit considers why we need money and how it contributes to economic activity. We will examine the role of financial institutions such as banks and stock exchanges in the world economy. Can you imagine a world without money?
How would firms pay their workers? How would we satisfy our needs and wants? How would the government be able to finance the building of new schools and hospitals?
We will begin by examining the functions of money and the need for exchange.
How would firms pay their workers? How would we satisfy our needs and wants? How would the government be able to finance the building of new schools and hospitals?
We will begin by examining the functions of money and the need for exchange.
Unit 3 Plan
| Economics Unit 3 Plan Printable Version |
What is Money?
Sample Class Activities
|
| ||||
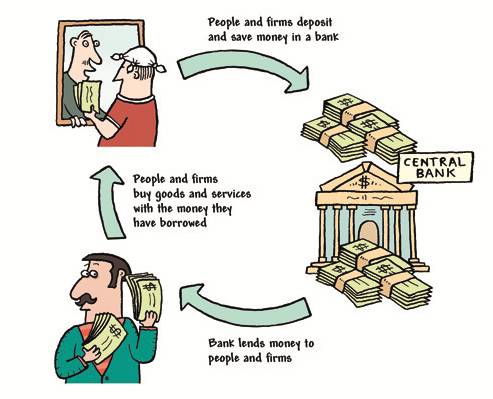
What is a bank?
How the Stock Market Works
The functions of money, banks and the stock market - Review
Occupations and Earnings
In this part of the unit you will study the following:
- factors that affect an individuals choice of occupation
- how wage rates are determined by the demand for labour and supply of labour to different occupations
- the differences in earnings between different occupational groups
- how and why governments may intervene in labour markets
- the benefits and disadvantages of specialization for the individual
|
|
| ||||||
The Financial Services Industry
This is the final part of Unit 3 and during this section we will study:
- analyse the different motives for spending, saving and borrowing.
- learn how age, tastes and consumer confidence affect our spending patterns.
- analyse the impact of changes in interest rates and the availability of credit can have on decisions to borrow money.
- look at how different income groups have different expenditure patterns.