Political Empowerment
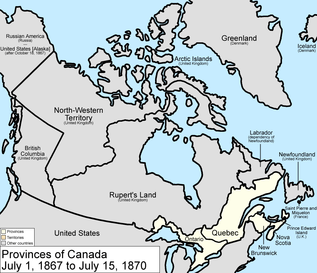
During this unit we will chart the evolution of Canada from being a largely British colony in the 1850's to the creation of the Dominion of Canada in 1867 (see pic) to the more recognizable provincial make-up of today.
We will also examine the distribution of the different groups within British North America in the 1850s: The British, the Irish, Black Colonists, First Nations, French Settlers, Acadians and the Metis. You will compare their different political rights and how they led the force for change to remove the British and to institute a 'fairer' type of government. diverse peoples living within what is now Canada during this period.
You will learn that different groups were politically empowered to varying degrees. The political structures in place empowered a very few and disempowered many, including Aboriginals and African-Canadians. The struggle to achieve responsible government was a process in which increasingly large numbers of people sought greater political power. Many internal and external factors affected this struggle.
We will also examine the distribution of the different groups within British North America in the 1850s: The British, the Irish, Black Colonists, First Nations, French Settlers, Acadians and the Metis. You will compare their different political rights and how they led the force for change to remove the British and to institute a 'fairer' type of government. diverse peoples living within what is now Canada during this period.
You will learn that different groups were politically empowered to varying degrees. The political structures in place empowered a very few and disempowered many, including Aboriginals and African-Canadians. The struggle to achieve responsible government was a process in which increasingly large numbers of people sought greater political power. Many internal and external factors affected this struggle.
Sample Classroom Activities
|
|
| ||||||
Unit 3 Lesson Plans
| G7 Unit 3 Plan Printable Version |
The Peoples of BNA Assignment: Exemplars
How To Use Google Presentation
|
Read through the attached document for guidance on how to use Google Presentation
|
| ||
The Push for Political Change
In the 1830's, some people in British North America were starting to resent all the power the Elite had. They didn't think it was fair, and they wanted change. The push for change didn't only come from those most in poverty (the Black Colonists, First Nations, Metis, etc) as they were more concerned with making sure they had enough to eat. The push for change came from the professional people who were educated. These people were called reformers.
What was the government like in the 1830's? Based on our studies of democracy, how democratic was it?
What was the government like in the 1830's? Based on our studies of democracy, how democratic was it?
|
|
The Legislative and Executive Councils
The Legislative Assembly
The Voters
|
Preceden Online Timelines

Go to the following website http://www.preceden.com/ and login using the following details:
Username: [email protected]
Password: cisjapan123
Practice using it for 10-15 minutes by making a short timeline of your life at CIS.
Username: [email protected]
Password: cisjapan123
Practice using it for 10-15 minutes by making a short timeline of your life at CIS.
